|
Bernhard Dobberstein
Dr. rer. nat. Universität Bonn
Postdoc: Rockefeller University, New York
Group leader EMBL Heidelberg
Since 1993 Professor at ZMBH Universität Heidelberg
Protein Targeting to the ER and Intracellular Sorting
Current Research
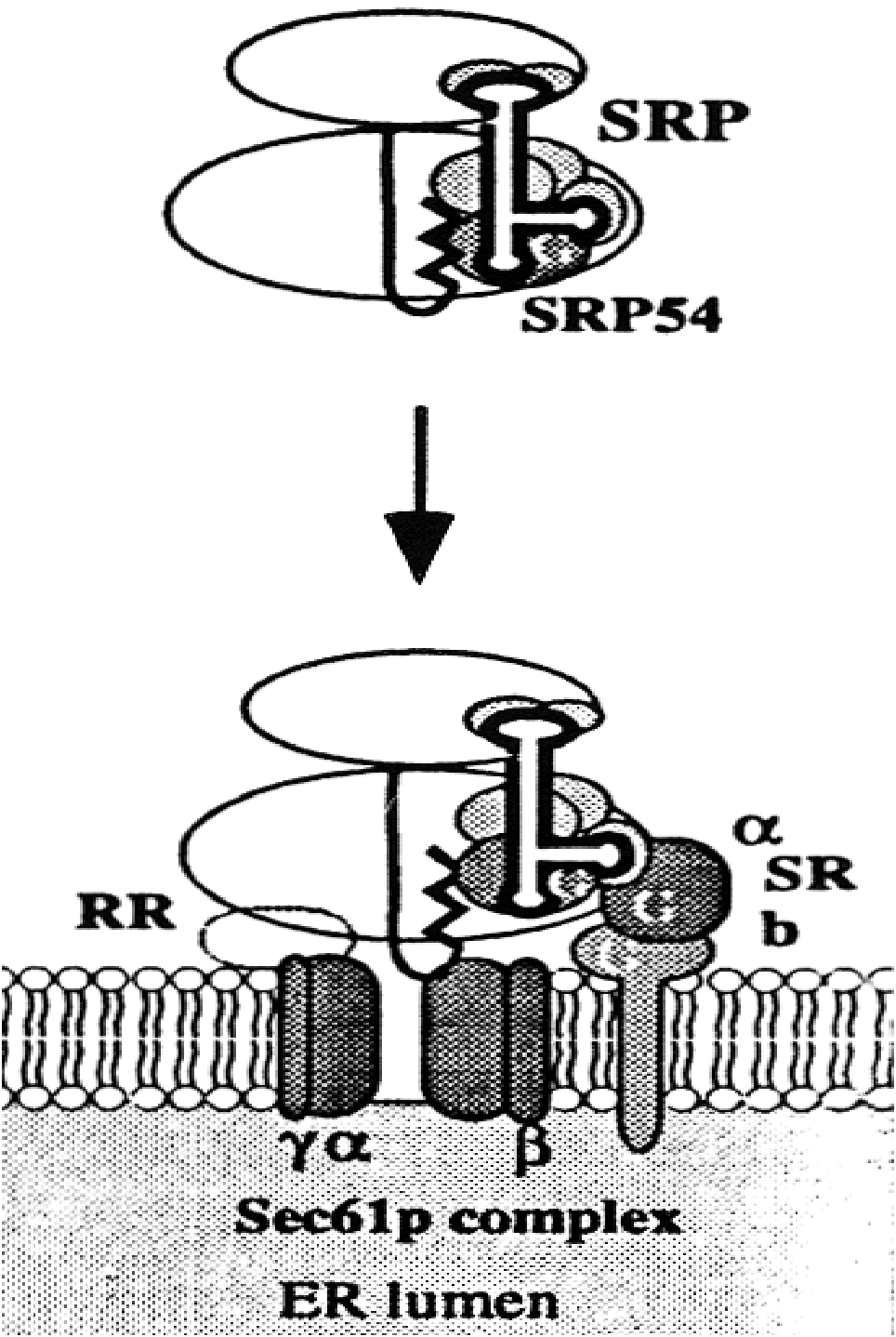
Protein translocation across the membrane of the endoplasmic
reticulum (ER) involves cytosolic chaperones, docking receptors,
a translocation channel (translocon) and in some cases a "translocation
motor" which drives the actual translocation (for review
see Schatz and Dobberstein, 1996, Science, 271, 1519-1526). Once
in the ER, proteins are folded, modified and - after a quality
control - packed into vesicles and transported to the Golgi complex
and the trans-Golgi network. From there they can either be further
transported to the plasma membrane or to organelles of the endosomal
system. A major focus of the work of the group is:
the analysis of mechanisms involved in targeting proteins to
the ER membrane and in their translocation across or insertion
into this membrane.
the control and regulation of protein translocation
the biosynthesis and intracellular sorting of the invariant chain
of MHC class II molecules.
Contact:
Bernhard Dobberstein
ZMBH
Im Neuenheimer Feld 282
69120 Heidelberg
Germany
Tel: - 49 - 6221 - 54 6825
Fax: - 49 - 6221 - 54 5892
E-mail: dobberstein@zmbh.uni-heidelberg.de
http://www.zmbh.uni-heidelberg.de/Dobberstein/default.html
 download download
|
|

Future Projects and Goals
Characterisation of the function of the 68 and 72 KDa proteins
of SRP.
Identification of alternative functions of signal sequences and
their fragments
Analysis of mechanisms that determine the multiple topologies
of prion protein in the ER membrane.
Analysis of the role of RAMP 4 in regulating protein modification
at the translocon
- Selected Publications
- Bacher et al. (1999). The ribosome regulates the GTPase of
the b-subunit of the signal recognition particle receptor. J.
Cell Biol. 146:723-730.
Schröder et al. (1999). Control of glycosylation of MHC
class II-associated invariant chain by translocon-associated
RAMP4. EMBO J. 18:4804-4815.
- Holscher et al. (2001) Prion protein contains a second ER
targeting signal located at ist C terminus. J. Biol. Chem. In
press
Martoglio and Dobberstein (1998) Signal sequences: more than
just greasy peptides, TICB 8, 410-415.
Martoglio and Dobberstein (1996) Snapshots of membrane - translocating
proteins TICB 6, 142 - 147.
Transport of protein
across the membrane
of the ER |
 |
|

